How to Get Rid of Spots: A Comprehensive Guide for Acne-Prone Skin
Acne, often a frustrating skin condition, affects people of all ages and skin types. From oily skin to severe acne breakouts, understanding how to get rid of spots is essential for achieving healthier, clearer skin. If you’re struggling with symptoms such as whiteheads, cysts, or blackheads, this guide will walk you through some of the most effective acne treatments, ingredients, and skincare tips to help you treat pimples and reduce acne scars.
How to Get Rid of Spots: Understanding Acne and Its Causes
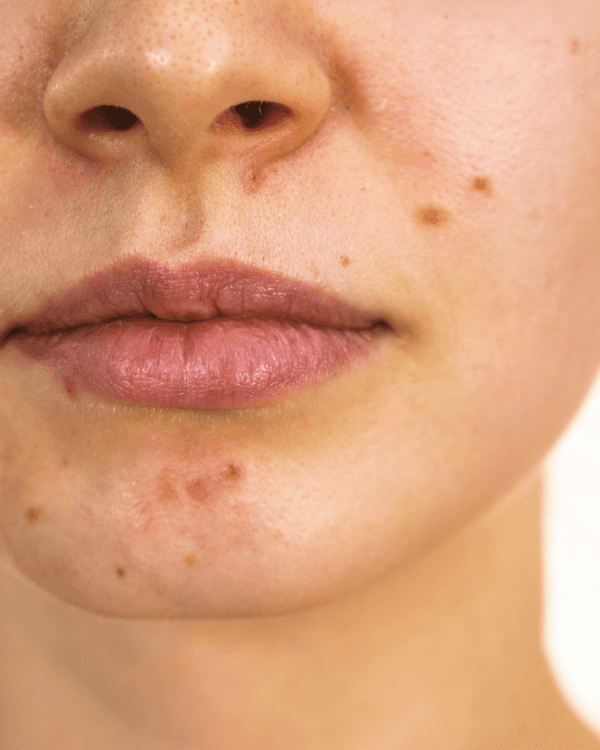
Acne vulgaris, the most common form of acne, occurs when hair follicles become clogged with a usually harmless skin bacterium called Propionibacterium acnes. This leads to the development of whiteheads, blackheads, pustules, and sometimes painful cysts. Acne can appear on various areas of the body, including the face, chest, and back.
The combination of excess oil, clogged pores, and acne-causing bacteria can lead to more severe acne, which may require specific treatments. Acne-prone skin often deals with the challenge of keeping excess oil in check while avoiding skin irritation, redness, and long-term damage like acne scarring.
Common Acne Triggers
Several factors contribute to the development of acne, including:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to acne flares.
- Sebum production: Overactive sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum, which can clog hair follicles. This combination of sebum and skin cells can lead to the formation of acne lesions like whiteheads and blackheads.
- Skin bacteria: While generally harmless, bacteria trapped in pores can cause inflammation and infection.
- Dead skin cells: When they aren’t properly removed, they can clog pores, leading to acne breakouts.
Diagnosing Acne
Diagnosing acne typically involves a thorough examination of the skin by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. During the consultation, the dermatologist will look for common signs of acne, such as blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. These observations help in classifying the severity of acne into four grades: mild, moderate, severe, and very severe.
To get a comprehensive understanding of your acne, the dermatologist may ask about your medical history, lifestyle, and skincare routine. This information can be crucial in identifying underlying causes, such as hormonal imbalances or specific skincare products that might be clogging your pores. In some cases, a skin scraping or biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions that resemble acne.
How to Get Rid of Spots: Top Ingredients and Treatments Including Benzoyl Peroxide
-
Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is one of the most effective acne treatments available. It works by killing bacteria, reducing inflammation, and helping to clear pores. This ingredient is especially useful for treating mild to severe acne, including whiteheads and pustules. However, benzoyl peroxide can cause dryness and skin irritation, especially for sensitive skin. To prevent further irritation, it’s essential to use a moisturizer and apply benzoyl peroxide sparingly.
-
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) that helps to remove dead skin and unclog pores. It penetrates deep into the hair follicle, making it ideal for treating acne-prone and oily skin. Regular use of salicylic acid can prevent acne breakouts and improve acne symptoms by exfoliating the skin and reducing inflammation.
-
Topical Retinoids
Topical retinoids, derived from vitamin A, are powerful tools for treating acne. They work by promoting skin cell turnover and preventing dead cells from clogging pores. When using topical retinoids, it’s essential to apply them sparingly to avoid skin irritation and peeling. Retinoids are especially effective for acne scarring and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is another excellent alternative treatment for acne. It helps to reduce inflammation, and kill bacteria. It’s also effective in treating skin conditions like rosacea and acne scars. Azelaic acid is less irritating than some other topical treatments, making it suitable for sensitive skin types.
-
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural remedy known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. It can be used as an alternative treatment for acne, particularly for mild irritation and blemish-prone skin. While it may not be as potent as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, tea tree oil can still help reduce acne-causing bacteria and improve acne symptoms.
-
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove old skin cells and promote the growth of new, healthier skin. This treatment is beneficial for acne scarring, pores, and skin texture. While mild irritation and skin redness can occur after a peel, the long-term benefits often include smoother, clearer skin.
-
Oral Antibiotics
For more severe acne, oral antibiotics like tetracyclines are often prescribed. These antibiotics help to reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the skin. It’s important to follow a healthcare provider’s advice when using oral antibiotics, as long-term use can lead to antibiotic resistance or side effects.
-
Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal treatments, including the combined oral contraceptive pill, are effective in treating acne that is related to hormonal imbalances. They work by regulating the hormones that cause excess oil production. However, it’s crucial to consult a doctor about potential side effects, such as an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
-
Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are applied directly to the skin to treat existing acne by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation. These treatments are often combined with other topical treatments like benzoyl peroxide for improvement in symptoms.
Tips for Managing Acne-Prone Skin
- Wash affected areas gently: Use a mild cleanser to wash your face and body twice a day. Avoid scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and make acne worse.
- Exfoliate regularly: Exfoliation helps to remove dead skin cells, which can prevent clogged skin and improve skin texture. Choose gentle exfoliants, especially if you have sensitive skin.
- Moisturize: Even if you have oily skin, moisturizing is crucial for maintaining skin health. Look for non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizers to avoid clogging pores.
- Wear sun cream: Sun exposure can lead to skin redness and worsen acne scars. Always wear a broad-spectrum sun cream to protect your skin.
- Avoid picking or popping pimples: This can lead to permanent scarring and worsen acne symptoms.
Preventing Acne
Preventing acne involves a combination of good skincare habits, a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding products that can clog pores. Start by keeping your skin clean; wash your face and body twice a day with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria. Opt for non-comedogenic products labeled “oil-free” or “non-acnegenic” to reduce the risk of clogged pores.
Avoid picking or popping pimples, as this can lead to scarring and increase the risk of infection. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support skin health and
Complications of Acne
Acne is more than just a cosmetic concern; it can lead to several complications, particularly when left untreated or improperly managed. In some cases, painful lesions like cysts can develop, often leaving behind acne scars. In addition to physical scarring, acne can cause emotional distress, particularly for people dealing with adult acne or persistent breakouts. One of the major complications arises when plugged hair follicles become infected, leading to deeper inflammation. If acne vulgaris is not properly addressed, chronic inflammation may result in long-term damage to the skin, including permanent scarring.
Topical creams, such as benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid, can help reduce symptoms by removing reducing oil production from sebaceous glands. However, improper or excessive use of treatments, like topical retinoids, can cause dry skin redness, and even worsen acne. For more severe cases, antibiotics like tetracyclines may be necessary to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
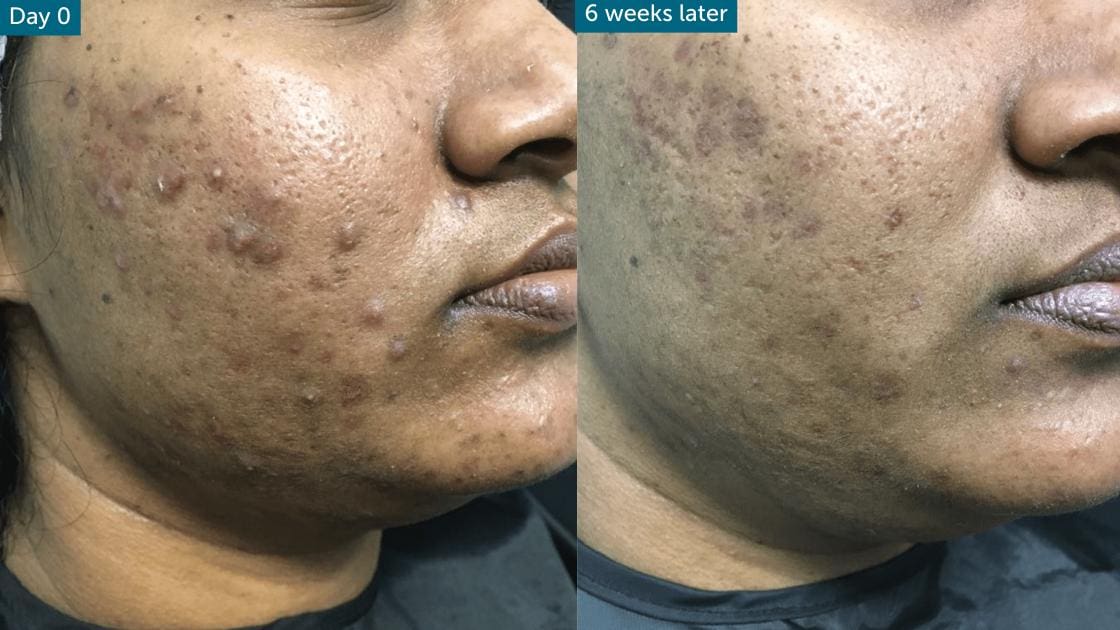
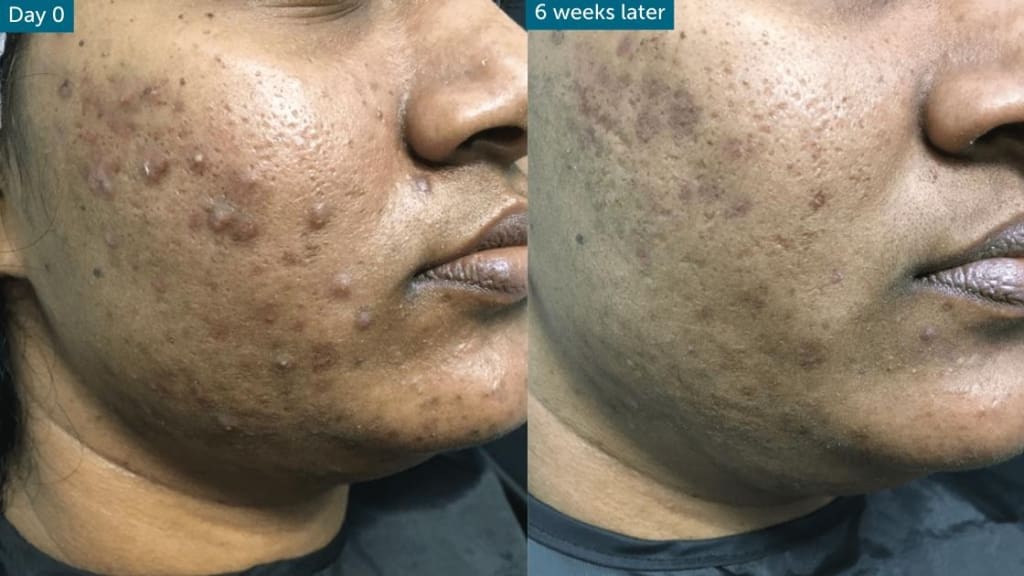
Treating Acne Scarring
For those who have battled acne, the scars it leaves behind can be a persistent reminder. Treating acne scarring is essential for restoring smooth skin texture and even tone. One effective approach is the use of skin peels, which help to promote skin peeling and the regeneration of new skin layers. These peels are particularly helpful for whiteheads and a few blackheads, as they help in removing dead skin cells and unclogging pores.
For deeper scars, treatments like salicylic acid and azelaic acid can offer gradual improvement by encouraging cell turnover and reducing inflammation. For acne that involves tender or sore pustules and cysts, hormonal treatment or antibiotics may first be necessary to clear active acne before addressing scars. Those with sensitive skin should proceed carefully with these treatments, as they may cause skin itchiness, tense skin, or irritation.
Acne Myths
When it comes to acne, there are countless myths that can mislead people searching for effective treatments. One common myth is that acne vulgaris is simply a result of poor hygiene. Another myth is that acne only affects teenagers. In truth, adult acne is quite common, and factors like stress, hormonal changes, and genetics play a significant role.
There’s also a misconception that using natural remedies like tea tree oil or over-exfoliating can quickly get rid of acne. While tea tree oil may help in mild cases, it’s not a substitute for more proven acne treatments like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, which work by removing dead skin cells. Additionally, excessive scrubbing or overuse can damage the skin’s barrier, leading to dry skin redness or worsened acne.
When to See a Dermatologist for Severe Acne
If you’re dealing with acne, painful cysts, or persistent acne scars, it may be time to consult a dermatologist. Treatments like hormonal therapies, oral antibiotics, and stronger topical treatments may be necessary to achieve significant improvement. Additionally, dermatologists can provide advice on acne scarring and suggest treatments like peels, laser therapy, or microneedling for permanent scarring.
Conclusion
Dealing with acne-prone skin requires a consistent skincare routine, patience, and the right products. By understanding how to get rid of spots and using ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and tea tree oil, you can treat acne effectively. For acne that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter treatments, seeing a dermatologist for personalized advice and prescription medications is a smart move to achieve clear, healthy skin.